在类 Unix 系统中,我们通常会配置 Shell 的 ~/.bashrc 或者 /etc/profile 来设置用户的工作环境。一般系统可能会有
/etc/profile
/etc/bashrc
/etc/bash.bashrc
~/.bashrc
~/.profile
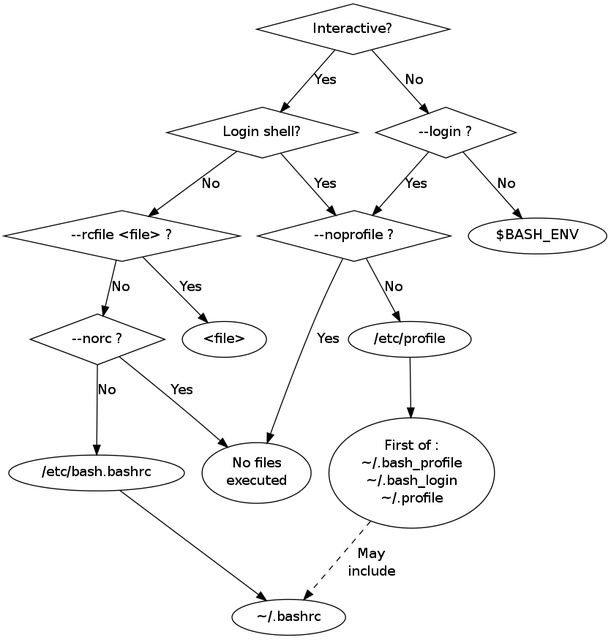
在理解这些文件之前,需要了解 Shell 不同的登录方式,login 登录和 interactive 模式。
关于 Shell 的历史和分类可以参考之前的文章
shell 不同启动方式
login shell
“login shell” 代表用户登入,比如使用 “su -“ 命令,或者用 ssh 连接到某一个服务器上,都会使用该用户默认 shell 启动 login shell 模式。
该模式下的 shell 会去自动执行 /etc/profile 和 ~/.profile 文件,但不会执行任何的 bashrc 文件,所以一般再 /etc/profile 或者 ~/.profile 里我们会手动去 source bashrc 文件。
启动场景:
- SSH 登录
sudo su -- 或者开启任何默认启动 bash 的终端
此时配置加载顺序
/etc/profile -> /etc/bash.bashrc
~/.profile -> ~/.bashrc
no-login shell
而 no-login shell 的情况是我们在终端下直接输入 bash 或者 bash -c “CMD” 来启动的 shell.
该模式下是不会自动去运行任何的 profile 文件。
/etc/bash.bashrc -> ~/.bashrc
interactive shell
交互式 shell 顾名思义就是用来和用户交互的,提供了命令提示符可以输入命令。
该模式下会存在一个叫 PS1 的环境变量,如果还不是 login shell 的则会去 source /etc/bash.bashrc 和 ~/.bashrc 文件
non-interactive
non-interactive shell 则一般是通过 bash -c “CMD” 来执行的 bash.
不会执行任何 rc 配置
四种方式区别
| 区别 | login | non-login |
|---|---|---|
| interactive | login 会加载 /etc/profile 和 ~/.profile ,interactive 会存在 PS1 变量 | 在终端中手动启动 bash, non-login 不会执行 profile,执行 /etc/bashrc 和 ~/.bashrc |
| non-interactive | login 会执行 profile ,non-interactive 不会执行 rc | bash -c “CMD” 执行,不会执行 profile ,也不会执行 rc |
区别
profile
profile 是某个用户唯一的用来设置环境变量的地方,因为可能有多个 shell 比如 bash 或者 zsh,但环境变量只需要统一初始化就行,这就是 profile 的作用
bashrc
用来给 bash 做初始化的,bash 的代码补全,bash 的别名,bash 的颜色,以此类推也就还会有 shrc, zshrc
通常一个好的做法是
/etc/profile是配置所有用户的~/.profile中配置和 bash 命令不是直接相关的内容,比如环境变量等等~/.bashrc中配置和交互式命令行相关的配置,比如命令自动补全,EDITOR 变量,bash aliases 别名等等~/.bash_profile可以当做~/.profile使用,只会被 bash 读取